| C8: a kind of bonded
phase commonly used
for reversed-phase chromatography; also called OCTYL.
|
||
| C18: a kind of
bonded phase commonly used for reversed-phase
chromatography; also called ODS or OCTADECYL.
|
||
| CALIBRATION: the
assignment of a value (the calibration factor or sensitivity
factor) to a
calibrator that allows determination of results by LC
analysis.
|
||
| CALIBRATION FACTOR:
as defined here, the calibration factor CF is equal to
the ratio of peak size of compound A in the calibrator to
the peak size of the internal standard in the calibrator
divided by the ratio of the concentration of compound A
in the calibrator to the concentration of the Internal
Standard in the calibrator. The concentration of A in a sample is then given as the ratio of the peak sizes in the sample divided by CF and multiplied by the concentration of Internal Standard added to the sample. See also INTERNAL STANDARD.
|
 |
|
| CALIBRATION PLOT:
for the external standard method, a plot of peak size (height
or area) on the y-axis (vertical) versus sample
concentration the x-axis (horizontal), using a series of
samples of known concentration (and equal injection
volumes). If the calibration plot is linear, it is
sometimes called the calibration line.
|
 The calibration plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between peak size and amount of analyte injected.
|
|
| CALIBRATOR: a
solution containing a known concentration of some
compound X that is to be determined in different samples
by LC analysis. See also STANDARD.
|
||
| CAM: a rotating
part attached to the pump motor and to the connecting rod
attached to the piston. See Pump.
|
 Cross-sectional diagram of a "generic" single-piston HPLC pump.
|
|
| CAPACITY FACTOR (k'): is one way to measure sample retention; bands which come out in the
chromatogram at the column dead time have a k'-value of
zero. Later bands have k'-values that increase with band
retention time. Values of k' for each band or compound
are constant if experimental conditions do not change. k'
does not change when flow rate or column dimensions are
changed. k' can change when mobile phase composition,
stationary phase chemistry, or temperature change. Also called the RETENTION FACTOR and symbolized by k (ASTM/IUPAC standard).
|
 k' is a measure of retention that is independent of flow and column dimensions.
|
|
| CHECK VALVE: a
device inserted into a moving liquid stream that allows
flow of the stream in only one direction. Check valves
are commonly built into the LC pump.
|
||
| "CHEMICAL
GARBAGE": contaminants in a sample that can
foul the LC column by irreversibly sticking to the bonded
phase.
|
||
| CHROMATOGRAM: a
plot or record of the chemical separation produced in
HPLC.
|
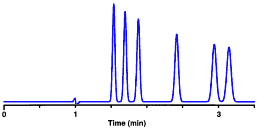 This chromatogram has 6 peaks. Ideally, each peak represents a single, unique analyte.
|
|
| CHROMATOGRAPHY: a
technique used to separate mixtures of chemical compounds
based on different rates of travel through a stationary
phase.
|
||
Flowing solvent (light blue) carries different analytes (green, blue red) through the column at different speeds.
|
||
| COLUMN: that part
of a chromatographic system where the separation of the
sample takes place.
|
 Waters Xterra Columns
|
|
| COLUMN DEAD-TIME
(t0): the time it takes for solvent
molecules or unretained sample bands (for which k'= 0) to
pass through the column. Uracil is often used to measure
t0 for reversed-phase columns.
|
||
| COLUMN PACKING:
the particulate material packed inside the column; also
called STATIONARY PHASE.
|
||
| COLUMN PLATE
NUMBER: See PLATE NUMBER.
|
||
| COLUMN VOID:
See VOID.
|
||
| CONTACT HEATER:
metal plates which wrap around an LC column and are
heated electrically. The heating is controlled to hold
the column at a constant temperature.
|
||
| CYANO: a type of
bonded phase use which can be used for either REVERSED-PHASE
LC or NORMAL-PHASE
LC.
|
||
