| NANOGRAM (ng): a unit
of mass, equal to one billionth of a gram. See Section 4B for relation to other units of mass.
|
||
| NANOMETER (nm): a unit
of length used to measure the wavelength of light used in
a photometric detector. See WAVELENGTH.
|
||
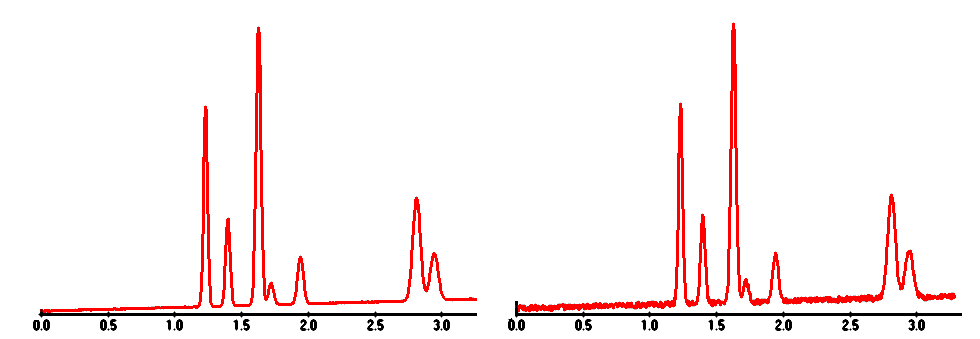
| NOISE: in HPLC
this usually refers to an irregular baseline that is hard
to measure; all baselines become "noisy" if the
attenuation of the detector is decreased enough. The two
chromatograms shown below differ only in the amount of
baseline noise |
||
|
||
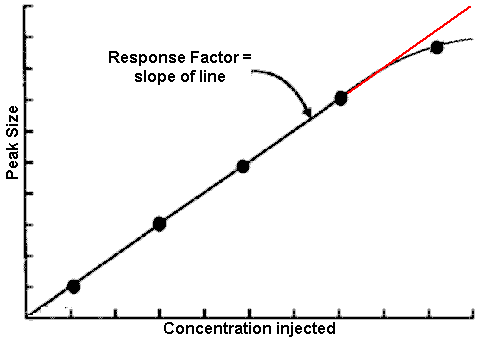
| NONLINEAR: an LC
method is said to be NONLINEAR when plots of peak-size vs
sample concentration are not straight lines. See LINEAR.
|
The calibration plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between peak size and amount of analyte injected.
|
|
| NONPOLAR:
compounds, solvents or bonded phases that dissolve
readily in solvents such as hexane or prefer such
solvents in place of water; nonpolar substances do not
dissolve in water. Nonpolar substances are often referred
to as HYDROPHOBIC.
|
||
| NORMAL-PHASE
LC: a less-common form of HPLC. Non-water-containing
mobile phases are used with special column packings that
have a hydrophilic surface layer.
|
||