| BAND: The distribution of an analyte
from the sample in the chromatographic system. When the
band passes through the detector, the result is a PEAK. In practice, the two terms are
often used interchangeably
|
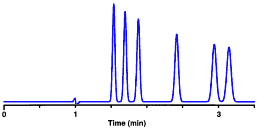 This chromatogram has 6 bands (peaks)
|
|
| BAND SIZE: See Peak
Height or Peak
Area.
|
||
| BAND WIDTH: The
width of the band measured at its base. Also called
BASELINE WIDTH.
|
 The "Baseline" width of a peak misses some area at the front and back!
|
|
| BAR: in HPLC a
unit of pressure, equal to one atmosphere; also equal to about 15 pounds per
square inch (psi) or 0.1 Megapascal.
|
||
| BASELINE: the
response of the detector on the data system display when no
sample band is passing through the detector.
|
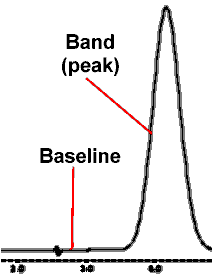 The "baseline" is the detector response when no sample is eluting from the column.
|
|
| BASELINE DRIFT: a
baseline that is not perfectly horizontal, but rises or
falls with time.
|
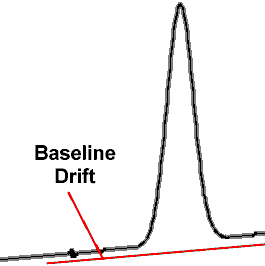 In the "real world", not all baselines are flat and horizontal.
|
|
| BASELINE WIDTH:
The width of the band measured at its base. Also called
BAND WIDTH.
|
||
| BATCH NUMBER: See LOT
NUMBER.
|
||
| BINARY-SOLVENT
MOBILE PHASE: a mobile
phase composed of
two solvents, such as methanol plus water. Most mobile
phases are of this type. Also called BINARY MOBILE PHASES.
|
||
| BODY: refers to the outside of a fitting, into which a nut screws. Also
called a Union. Most fittings used in HPLC are
characterized as "ZDV" (Zero Dead Volume).
|
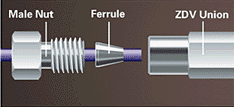 Upchurch tube end & fitting body (ZDV union)
|
|
| BONDED PHASE: the
layer of organic material that covers the surface of the pores inside of the stationary
phase particle, and
is responsible for the separation characteristics of an
LC column.
|
||