| DATA SYSTEM: a
versatile data processor that, can simultaneously serve
several different LC systems; it may also control some of
the system modules (pumps, detectors, etc.) and carry out
other functions.
|
||
| DATA PROCESSOR: a
module that converts the detector readings for an LC run
into final results: concentrations of each compound in
the sample, retention times for each band to permit
identification of each band in the chromatogram, etc. In
this course, data processors include integrators, data
systems, and computers.
|
||
| DEAD-TIME See COLUMN
DEAD-TIME.
|
||
| DEAD-VOLUME: small
spaces within the LC system where remixing of separated
sample bands occurs, or where the initial sample
is diluted with mobile phase. Extra-column dead-volume should be
minimized in an LC system, especially when small-volume
columns of high plate number are used.
|
||
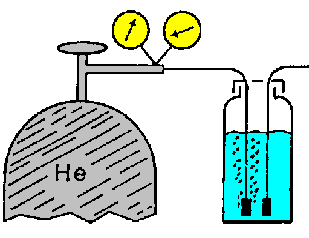
| DEGASSING: the
practice of removing air from the mobile phase; degassing
can be achieved by helium sparging, applying vacuum to the mobile
phase (either directly or across a semipermeable membrane),
ultrasonification, or heating.
|
Helium sparging is one of the most effective ways of removing dissolved gas from the mobile phase.
|
|
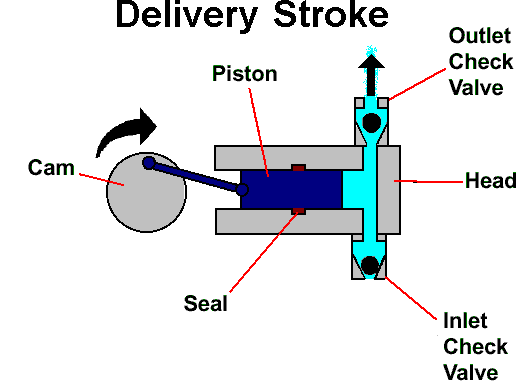
| DELIVERY STROKE:
movement of the pump piston so as to push mobile phase
into the lines leading to the injector and column.
|
 |
|
| DETECTOR: the LC
module that measures the concentration of sample bands as they leave the column, thus
furnishing a chromatogram.
|
 Waters 996 Photodiode Array Detector
|
|
| DILUTION FACTOR (DF):
for dilution of a sample by pipetting V1 mL of sample
into a volumetric flask of volume V2, the dilution factor
is equal to V2/V1; it is the ratio by which sample
concentrations in the original sample are decreased in
the diluted sample. The final (diluted) concentration C2
is related to the initial sample concentration C1 as C2 =
C1 / DF.
|
||
| DIOL: a type of
bonded phase use for NORMAL-PHASE LC.
|
||
| "DIRTY"
SAMPLES: samples obtained from biological,
environmental, or other sources that contain compounds
that might foul the LC column, by irreversibly sticking
to the bonded phase.
|
||