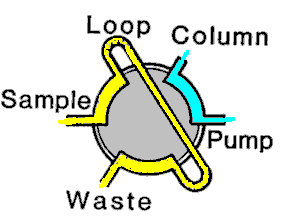
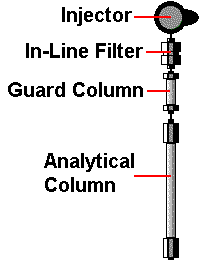
| INJECTOR: the 6-port
sample valve used to introduce a precise volume of sample
into the LC system. Also called an INJECTION VALVE.
|
Standard 6-port injector
|
|
| INLET CHECK VALVE:
the check valve on an LC pump that allows mobile phase to
flow from the reservoir to the pump, but not in the
reverse direction. See CHECK VALVE.
|
Cross-sectional diagram of a "generic" single-piston HPLC pump.
|
|
| INLET FILTERS: 10-micron
frits attached to the inlet lines to the
pump that filter the mobile phase entering the pump and
help anchor the inlet line in the reservoir . Also called
SINKERS. See RESERVOIR.
|
||
| IN-LINE FILTER: a frit (usually 0.5 or 2 micron porosity)
held in a container ("frit-holder") and
connected between the sample injector and LC (analytical)
column.
|
|
|
| INJECTION
SOLVENT: the solvent that the sample is
dissolved in before it is injected into the LC system.
|
||
| INJECTION
VALVE: see INJECTOR.
|
||
| INTAKE STROKE:
movement of the piston of a pump so as to draw mobile
phase into the pump cylinder from the reservoir.
|
|
|
| INTEGRATOR: a
module that measures the area of bands in an LC (or CC) chromatogram.
Integrators may also record the chromatogram, measure
retention times, and perform simple calculations.
|
||
| INTERFERENCE: an
unwanted peak that overlaps one of the desired peaks in a
chromatogram. Interferences reduce the reliability of the
results.
|
||
| INTERNAL
STANDARD: a compound added to calibrators and samples in order to improve
precision.
|
||
| INTERNAL
STANDARD METHOD: a calibration procedure that involves addition of
a compound (the "internal standard") to each
sample and calibrator to be run in a given LC analysis
procedure.
|
||
| ION EXCHANGE
CHROMATOGRAPHY: an HPLC method, different from
reversed-phase chromatography. This method uses water
solutions as the mobile phase and separates ions, acids
and bases.
|
||
| ION PAIR
CHROMATOGRAPHY: an HPLC method, different from
reversed- phase chromatography. It uses similar columns
and mobile phases, but is especially suited for
separations of acids and bases.
|
||
| ION PAIR
REAGENT: a compound that is added to the
mobile phase to carry out ion pair chromatography.
|
||
| ISOCRATIC: refers
to an HPLC separation where the mobile phase composition
stays the same during the run (the usual way LC is
carried out). Isocratic separations are the opposite of
gradient elution. Isocratic means "equal-strength"
in Greek, meaning that mobile phase strength stays
constant during the run. See also GRADIENT
ELUTION.
|
||