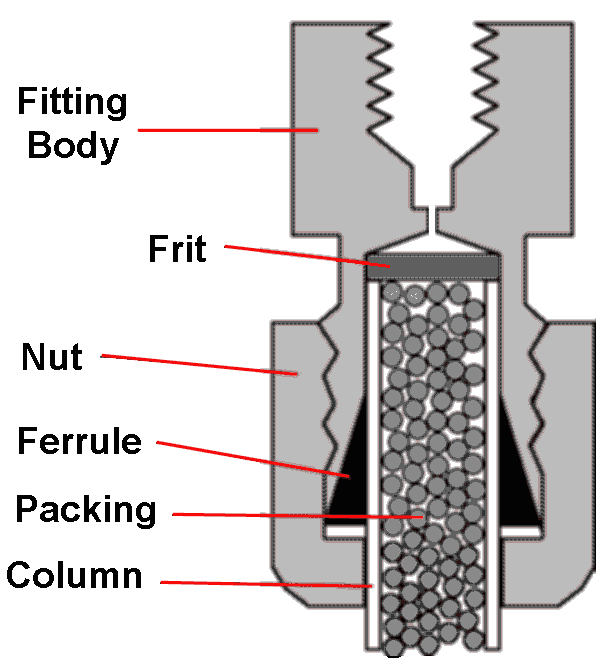
| PACKING: the
particles that fill the column; also called COLUMN
PACKING or
STATIONARY PHASE.
|
Generic Column End Fitting Cutaway
|
|
| PARTIAL-LOOP INJECTION: injection of a sample volume which
is smaller than the volume of the loop of the injector.
See also FILLED LOOP INJECTION
|
Partial-Loop Injection
|
|
| PARTICULATES:
usually refers to small solid particles in the sample or
mobile phase; these particles can plug the column or
other parts of the HPLC system.
|
||
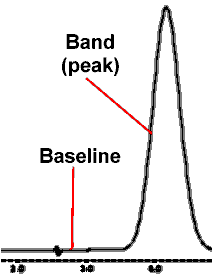
| PEAK: The deviation from baseline in a chromatogram caused by the properties of the analyte as it transits the detector cell. In practice, the terms peak and band are often used interchangeably; in principle, a band is the distribution of analyte molecules in the chromatographic system, while a peak is the trace detector response as the band passes through the detector. |
|
|
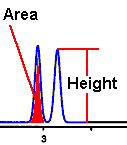
| PEAK AREA or HEIGHT : used to measure the size of the peak for use in quantitative analysis.
|
In most cases, either area or height measurements can be used for quantitation
|
|
| PEAK ASYMMETRY:
see ASYMMETRY FACTOR, TAILING
FACTOR.
|
||
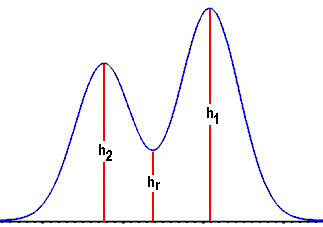
| PEAK VALLEY: the
lowest point between two adjacent peaks; the height of
the valley from the baseline (as a percent of the peak heights)
is a measure of how good the separation is.
|
|
|
| PHENYL: a kind of
bonded phase used for reversed-phase chromatography.
|
||
| PHOTOMETRIC
DETECTOR: the most commonly used LC detector, based on the passage of UV light
through a flow cell containing column effluent. The light
passing through the flow cell is converted into a plot of sample
concentration versus time (the chromatogram).
|
||
| PHOTODIODE
ARRAY DETECTOR: a photometric detector that allows
the selection of many simultaneous wavelengths for detection (usually in the range
from 190 to 360 nm).
|
||
| PICOGRAM (pg):
a unit of mass, equal to a trillionth of a gram. See Section 4B for the relation to other units of
mass.
|
||
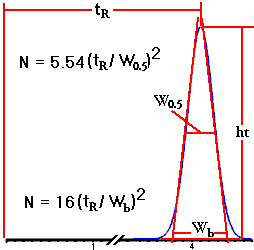
| PLATE NUMBER (N): a
number that describes how good a column is in keeping
sample bands narrow. Columns with large plate
numbers give narrow bands; long columns packed with small
particles give the highest plate numbers.
|
For a perfectly symmetrical peak, both of these calculations should yield the same value for N
|
|
| POLAR:
compounds, solvents or bonded phases that dissolve in
water or prefer water to nonpolar organic solvents such as hexane.
|
||
| POLAR-BONDED-PHASE
CHROMATOGRAPHY: another HPLC method, different
from reversed-phase chromatography. Mobile phases that do
not contain water are used with this method. Most polar-bonded
phase separations are classed as NORMAL-PHASE
CHROMATOGRAPHY.
|
||
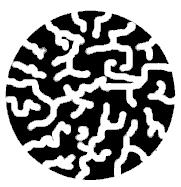
| PORE: the particles of column packing
are in most cases porous, meaning that each particle has
small tunnels or "pores" that criss-cross or
"honeycomb" the particle; sample molecules that
are retained by the particle or stationary
phase enter these
pores and interact with the inside of the particle.
|
Most HPLC packings are porous. Most of the stationary phase surface area is on the inside of the particles.
|
|
| PRECISION: the
extent to which results from LC analysis cluster about
the same value, so that repetitive analysis of the same
sample gives similar results. Precise values are not
necessarily accurate or "correct". See Accuracy.
|
Accuracy and Precision are not the same thing!
|
|
| PRECOLUMN: a
column (usually packed with silica) that is connected
between the pump and the sample injector. The precolumn
is normally intended to precondition the mobile
phase in order to
minimize chemical attack by the mobile phase on the
column packing.
|
||
| PREPARATIVE
COLUMN: a larger-diameter column used for
recovering purified materials by chromatographic
separation. Can be contrasted with "analytical
columns" that
are used mainly for analysis, rather than recovery of
fractions.
|
||
| PRESSURE: the
reading given by a gauge, meter, or other read-out device
for an LC system; this is the pressure measured between
the pump and column, and usually measures the pressure
drop across the column.
|
||
| PUMP: the LC
module that delivers mobile phase to the injector and column.
|
Cross-sectional diagram of a "generic" single-piston HPLC pump.
|
|